Apprenticeships are a great way to start your career after school or college!
How do Apprenticeships work?
There are three key participants on an Apprenticeship; the apprentice; the employer and the Apprenticeship Training Provider.
- The apprentice – is employed by an organisation and receives training and support from the Training Provider.
- The employer – provides a contract of employment (this may be a fixed term contract) and has an agreement in place to support the delivery of the Apprenticeship alongside the Apprenticeship Training Provider. The contract of employment will contain the same rights and responsibilities as any other “non-apprentice” e.g. annual leave entitlements.
- The Apprenticeship Training Provider – could be an Independent Training Provider, a Further Education College, an Employer Provider or a University. They provide the apprentice with training and support they need to succeed in their Apprenticeship.
The Apprenticeship Pay Survey 2018/19 – England, states that the mean salary of an apprentice aged 16-18 is £5.34 per hour. More information on National Apprenticeship Wage and National Minimum Wage can be found here.
20% Off-the-Job Training
20% of your time throughout your apprenticeship will be spent with your training provider learning new skills “off-the-job” and working towards your qualification. This could mean you have 1 day a week to do any training either at work or at a training centre, or it could be delivered in “blocks” – this would be decided by the employer and training provider.
End Point Assessment
Before completing an apprenticeship, apprentices are required to undertake an End Point Assessment (EPA). The EPA is different for each apprenticeship standard but could consist of a presentation, an observed practical assessment, a written and or multiple choice test, an interview or another method of assessment. The EPA will test both your academic learning and occupational competence, which essentially means they will be looking for you to provide evidence and examples that demonstrate that you know how to perform your job.
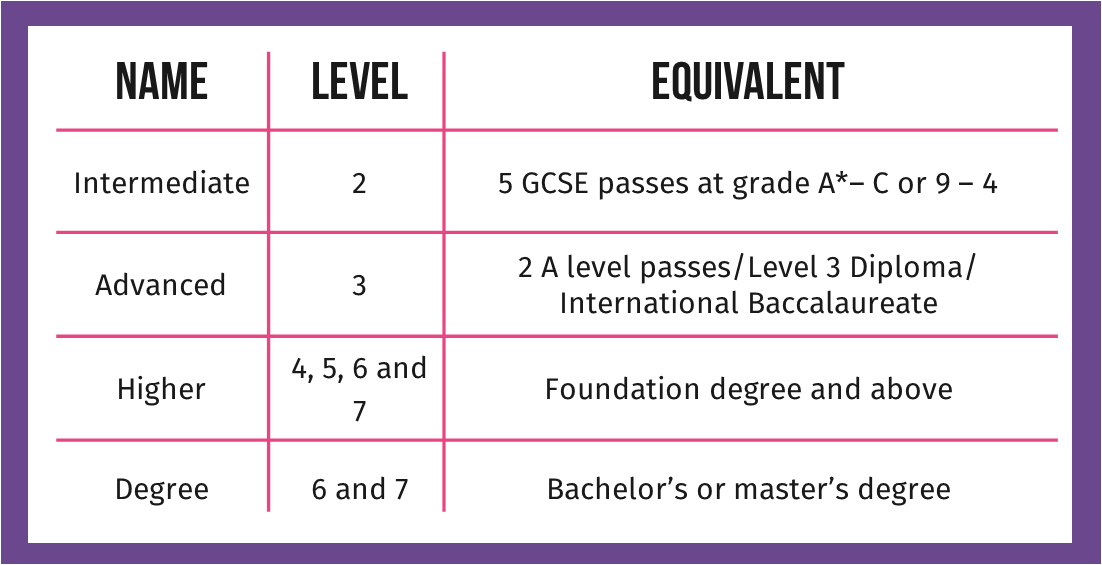
Levels
- An Intermediate (Level 2) Apprenticeship is equivalent to 5 GCSE passes at grade A*-C or 9-4.
- An Advanced (Level 3) Apprenticeship is equivalent to 2 A Level passes, Level 3 Diploma or an International Baccalaureate.
- A Higher (Level 4-7) Apprenticeship is equivalent to a Foundation Degree and above.
- A Degree (Level 6-7) Apprenticeship is equivalent to a Bachelor’s or Master’s Degree.
How to Apply
- Greater Manchester Apprenticeship & Careers Service (GMCAS) allows you to find our further information and consider Apprenticeships alongside all of your other options for training and study when you leave school. It also providers a platform for you to apply when you are ready!
- Another great to start looking is the Find an Apprenticeship website. You can search by what type of Apprenticeship you want to do, as well as the level and location etc.
- If you have already found an employer that is willing to take you on as an apprentice, they may already have an Apprenticeship Training Provider that they work with and if so, they can have a chat with them. If not, then they can start to look on the Find an Apprenticeship Training Provider website.
Hear from Apprentices:
Charlie started with Allied Vehicle Service on a work experience scheme through school. He certainly left an impression on Thomas as they went on to offer him a Level 2 Motor Vehicle Apprenticeship! Click here to watch Charlie’s video to find out more.